In the world of material analysis, the laboratory sample pulverizer plays a vital role. Experts like Dr. Emily Hartman, a leading figure in material science, state, "A reliable pulverizer can reveal the true composition of materials." This statement underscores the importance of such equipment in laboratories.
laboratory sample pulverizers are designed to crush and grind samples into a fine powder. This process allows scientists to conduct accurate analyses. For instance, the pulverizer’s mechanics involve the use of rotating blades or mills, ensuring uniform particle size. However, not every pulverizer achieves this flawlessly. Some may produce inconsistent results, which can mislead researchers.
Detailing the operation of a laboratory sample pulverizer reveals its significance. It transforms various substances, from minerals to chemicals, into a manageable form. The functionality, while seemingly straightforward, often requires adjustments. The calibration of settings can lead to debates among researchers about optimal conditions. While the technology has advanced, challenges remain in achieving the perfect grind every time.
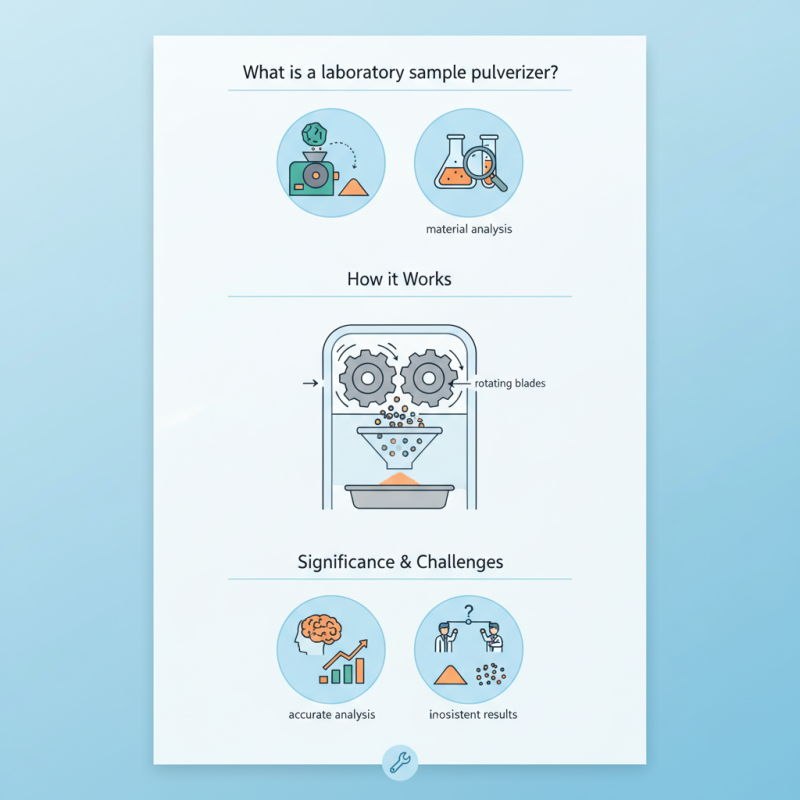
A laboratory sample pulverizer is a vital tool for material analysis. It grinds samples into finer particles. The main purpose is to prepare materials for various tests. These tests can include chemical analysis or physical property assessments.
Understanding how a pulverizer works is essential. Samples are placed in the machine's grinding chamber. A rotating mechanism crushes these samples into smaller sizes. This process usually takes a few minutes. However, some materials may need longer grinding times. The end result is a uniform powder, suitable for testing.
Despite its utility, there are challenges. Some materials may create excessive dust. This can interfere with the grinding process and affect results. Operators must watch for overheating as well. Regular maintenance of the device is crucial. Oversights can lead to inaccurate results and wasted materials. Each sample must be handled with care to ensure reliability.
Laboratory sample pulverizers are essential tools in material testing. They come in various types, each designed for specific applications. The most common types include impact pulverizers, ball mills, and cryogenic grinders. Impact pulverizers use high-speed force to crush samples, making them ideal for soft materials. Ball mills, on the other hand, grind materials into fine powders through a rotational action. Cryogenic grinders freeze samples to make them brittle. This allows for easier grinding of tough materials.
When selecting a pulverizer, consider the material type and desired particle size. Soft materials may not require as much force, whereas hard materials might need a more robust pulverizer. Be mindful of the sample quantity as well. A small sample may not yield a representative particle size using a large machine.
Tips: Always wear safety gear when operating any pulverizer. Monitor the temperature and avoid overheating during grinding. Check the machine's maintenance needs regularly. This ensures optimal performance and extends its lifespan. Discrepancies in expected outcomes may result from improper usage. A little care can make a big difference in your results.
| Type of Pulverizer | Working Principle | Applications | Material Types |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jaw Pulverizer | Crushing action using a stationary jaw and a moving jaw. | Rock and mineral analysis. | Hard rocks, ores. |
| Hammer Mill | Impact-based grinding using high-speed rotating hammers. | Food and chemical sample preparation. | Grains, spices, soft minerals. |
| Disc Mill | Grinding by friction and pressure between two flat discs. | Plastic and metal sample preparation. | Plastics, soft metals. |
| Mortar and Pestle | Manual grinding using a bowl (mortar) and a heavy tool (pestle). | Small-scale sample preparation. | Herbs, small minerals, laboratory chemicals. |
| Planetary Ball Mill | High-energy milling using balls in a rotating chamber. | Material synthesis and nanomaterial preparation. | Ceramics, metals, composites. |
Laboratory sample pulverizers are pivotal in material research and analysis. These devices are designed to reduce the size of solid samples for various tests. Typically, they work by employing mechanical forces to break down materials into smaller particles. The most common methods include crushing, grinding, and milling. The efficiency of these processes can significantly affect the results of subsequent analyses.
The working principle hinges on the mechanism of impact and attrition. As the sample is placed inside a chamber, a rotating element generates collisions that pulverize the material. According to a report by the American Society for Testing and Materials, controlling particle size consistency is crucial. Inconsistent sizes can lead to varied testing outcomes, undermining the reliability of the data collected. Studies suggest that samples must often reach sizes below 75 microns for accurate analysis, which challenges traditional methods and raises concerns over efficiency and excess energy use.
Despite advancements, achieving perfect particle reduction remains elusive. Variability due to the material type and hardness can affect performance. It is not uncommon for some lighter materials to produce dust rather than uniform particles. Reflecting on these challenges can lead to improvements in design and operational protocols. Ongoing research aims to enhance the mechanisms not only for efficiency but also for the precision of results.
Laboratory sample pulverizers are essential in various scientific fields. They help prepare materials for analysis. Effective pulverizers need specific features for optimal performance. One key aspect is their crushing capacity. A well-designed pulverizer can reduce particle size to less than 100 microns. According to research, achieving this level of fineness can significantly enhance analytical accuracy.
Another important specification is the speed of operation. Some models can reach speeds up to 3000 rpm. This high-speed function allows for efficient processing. However, there is a catch. Increased speed may lead to heat generation, affecting sample integrity. Proper cooling mechanisms are often overlooked, yet essential.
Durability is also vital. Using high-quality materials ensures that pulverizers withstand heavy use. Data indicates that machines with reinforced components last significantly longer. Regular maintenance is crucial but frequently neglected. Inadequate upkeep can lead to subpar performance and increased costs. Awareness of these aspects can enhance the effectiveness of laboratory pulverization processes.
Maintenance is crucial for the longevity of laboratory pulverizers. Regularly check the blades for wear and tear. Worn blades can lead to uneven particle size and lower efficiency. It is advisable to clean the internal components after each use. Dust particles can accumulate, affecting performance and accuracy. Neglecting this can lead to contamination of future samples.
Safety considerations are equally important. Ensure that safety guards are in place during operation. These guards prevent accidental injuries. Ear protection is also recommended, as pulverizers can be noisy. Always work in a well-ventilated area. Some materials may release harmful dust when pulverized. Training personnel on proper usage can mitigate risks. Remember, safe operation is everyone’s responsibility.
